SI joint exercises improve sacroiliac stability and alleviate pain․ Gentle stretches and mobilizations, like the single knee-to-chest stretch, promote healing․ Guidelines ensure pain-free practice, enhancing joint function and overall mobility naturally․
1․1 What is the SI Joint?
The sacroiliac (SI) joint connects the sacrum (base of the spine) to the ilium (pelvic bone), forming a critical link between the spine and pelvis․ It plays a key role in weight distribution, absorbing forces during movement․ The joint is irregularly shaped, providing stability while allowing limited motion․ Its proper function is essential for maintaining pelvic alignment and facilitating activities like walking and sitting comfortably․ Understanding its structure and role aids in addressing related pain and dysfunction effectively․
1․2 Importance of SI Joint Stability
SI joint stability is crucial for maintaining proper pelvic alignment and supporting the body during movement․ It ensures even weight distribution, reducing strain on the lower back and hips․ Stable SI joints enhance posture, improve mobility, and prevent dysfunction․ Instability can lead to pain and discomfort, affecting daily activities․ Strengthening the surrounding muscles and ligaments is vital for long-term joint health and overall musculoskeletal well-being․ Achieving stability promotes pain-free movement and enhances quality of life․
1․3 Benefits of SI Joint Exercises
SI joint exercises offer numerous benefits, including pain reduction, improved mobility, and enhanced joint function․ They strengthen surrounding muscles, improve posture, and promote healing naturally․ Regular practice can prevent future discomfort and improve overall quality of life․ By addressing instability and inflammation effectively, these exercises support long-term musculoskeletal health and well-being․

Common Causes of SI Joint Pain
SI joint pain often arises from inflammation, trauma, or biomechanical issues․ Pregnancy-related hormonal changes and muscle imbalances can also contribute to sacroiliac dysfunction and discomfort․
2․1 Inflammation and Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Inflammation in the sacroiliac joint can lead to dysfunction, causing pain and stiffness․ It often results from repetitive strain or underlying conditions like arthritis․ Swelling and irritation disrupt the joint’s normal functioning, leading to instability and discomfort․ Addressing inflammation through targeted exercises and therapies is crucial to restoring joint health and reducing pain․
2․2 Trauma or Injury to the Pelvis
Trauma or injury to the pelvis can disrupt the sacroiliac joint, leading to pain and instability․ Accidents, falls, or sudden impacts can cause misalignment or inflammation․ Such injuries often result in limited mobility and discomfort․ Addressing these issues through targeted exercises and therapies is essential to restore joint stability and alleviate pain effectively․
2․3 Biomechanical Issues and Muscle Imbalances
Biomechanical issues and muscle imbalances can strain the sacroiliac joint, leading to pain and dysfunction․ Weak core muscles, tight hip flexors, or poor posture can disrupt joint alignment․ These imbalances often result in uneven stress on the SI joint, causing inflammation and discomfort․ Addressing these issues through targeted exercises, such as pelvic tilts and stretches, can help restore proper biomechanics and alleviate pain effectively, improving joint stability and overall mobility․ Regular practice is key to maintaining balance and preventing further discomfort․
2․4 Pregnancy and Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy and hormonal changes can weaken sacroiliac joint stability, leading to pain and discomfort․ Hormonal shifts relax ligaments, increasing joint mobility and stress․ Weight gain and posture changes during pregnancy further strain the SI joint, causing inflammation and instability․ These factors often result in SI joint dysfunction, which can persist postpartum․ Addressing these issues with targeted exercises and proper care is crucial for alleviating discomfort and restoring joint function during and after pregnancy․

Key Principles of SI Joint Exercise Programs
SI joint exercises focus on pain-free movements, gradual progression, and breathing techniques to enhance stability․ Core strength and proper alignment are prioritized to ensure safe and effective practice․
3․1 Pain-Free Exercise Guidelines
Exercises should be performed within a pain-free range, ensuring discomfort does not exceed 4/10․ Start slowly, easing off if pain occurs․ Activities like walking or cycling are beneficial, while prolonged rest should be avoided․ Avoid movements that aggravate symptoms, and modify exercises to suit individual tolerance․ Prioritize gentle, controlled motions to promote healing and stability without causing further strain on the sacroiliac joint․
3․2 Progression of Exercises
SI joint exercises progress through three phases to ensure safe and effective rehabilitation․ Phase 1 focuses on gentle stretches and mobilizations, such as knee-to-chest stretches and pelvic tilts, to improve flexibility without causing pain․ Phase 2 introduces strengthening exercises like glute bridges and bird dog exercises to build stability․ Phase 3 advances to dynamic stabilization with single-leg stances and step-ups, promoting functional strength and balance․ Gradual progression ensures exercises remain challenging yet safe, fostering long-term joint health and mobility․
3․3 Breathing Techniques During Exercises
Proper breathing is essential during SI joint exercises to enhance relaxation and maintain proper form․ Deep belly breathing helps stabilize the core and reduces muscle tension․ Inhale slowly through the nose, allowing the abdomen to rise, and exhale gently through the mouth․ This technique promotes pelvic stability and prevents excessive movement during exercises․ Coordinating breath with movement ensures optimal alignment and minimizes discomfort, fostering a safe and effective exercise routine for SI joint health․
3․4 Importance of Core Stability
Core stability is crucial for SI joint exercises as it provides a solid foundation for movement․ Strengthening abdominal and pelvic muscles enhances pelvic alignment, reducing SI joint strain․ A stable core improves posture, promotes even weight distribution, and minimizes excessive joint movement․ Incorporating exercises like planks, bird dog, and pelvic tilts can help maintain core strength, ensuring safer and more effective SI joint exercises․ This stability is key to preventing injury and optimizing the benefits of your exercise routine․

Phase 1: Gentle Stretches and Mobilizations
Phase 1 focuses on gentle stretches and mobilizations to improve SI joint flexibility and comfort․ Exercises like single knee-to-chest stretches and pelvic tilts promote healing without pain, ensuring a safe foundation for progress․ These activities are designed to enhance mobility while maintaining joint stability, making them ideal for initial recovery and strengthening․ Consistency in these exercises is key to improving SI joint stability and reducing discomfort effectively․
4․1 Knee-to-Chest Stretch
The knee-to-chest stretch is a foundational exercise for SI joint mobility․ Lie on your back, bring one knee toward your chest, and gently pull it with your hands or a strap․ Hold for 20-30 seconds, then release․ Repeat 3 times on each side․ This stretch targets the sacroiliac joint, relieving tension and improving flexibility․ Perform slowly and within a pain-free range to avoid discomfort․ If needed, modify by bending the knee slightly to reduce strain while maintaining the stretch’s benefits for joint stability and relaxation․
4․2 Pelvic Tilt Exercise
The pelvic tilt exercise is a gentle movement that targets the sacroiliac joint and lower back․ Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor․ Engage your core and tilt your pelvis upward, flattening your lower back against the ground․ Hold for 5 seconds, then release․ Repeat 10-15 times․ This exercise improves pelvic mobility and strengthens surrounding muscles, enhancing SI joint stability․ Perform slowly and within a pain-free range to maximize benefits and avoid discomfort․
4․3 Sacroiliac Joint Mobilization Techniques
Sacroiliac joint mobilization involves gentle, controlled movements to improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness․ Techniques include diagonal tilting of the pelvis and self-mobilization using a belt or towel․ Lie on your back, place the belt around your pelvis, and gently pull to create a diagonal stretch․ Perform 5-10 repetitions, focusing on pain-free movement․ These exercises enhance joint function and promote relaxation of surrounding muscles, aiding in overall SI joint stability and comfort․ Practice 2-3 times daily for optimal results․
4․4 Cat-Cow Spine Mobilization
Begin on your hands and knees․ Arch your back, lifting your head and tailbone (cow pose), then round your spine, tucking your chin and pelvis (cat pose)․ Move slowly, focusing on a smooth transition between positions; Repeat 10-15 times․ This exercise enhances spinal flexibility and relieves sacroiliac tension․ Perform it pain-free, stopping if discomfort arises․ Practice daily to improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness in the lower back and pelvis, supporting SI joint stability and overall posture․

Phase 2: Strengthening Exercises
Phase 2 focuses on strengthening exercises to enhance SI joint stability and surrounding muscle support․ Exercises like glute bridges, bird dog, and side planks improve hip and core strength, reducing pain and promoting joint stability․ These activities build on the foundation of Phase 1, progressing toward functional movements that enhance overall pelvic and spinal alignment․ Regular practice strengthens the muscles, providing long-term relief and preventing future discomfort․ Consistency is key for optimal results and sustained joint health․
5․1 Glute Bridges for Hip Stability
Glute bridges are an effective exercise for strengthening the gluteus maximus, which plays a crucial role in hip stability and SI joint health․ To perform, lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor․ Slowly lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top, then lower back down․ Start with 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, gradually increasing as strength improves․ This exercise enhances posterior chain strength, improves posture, and reduces strain on the SI joint․ Consistency is key for long-term benefits․
5․2 Bird Dog Exercise for Core Strength
The Bird Dog exercise strengthens the core and improves SI joint stability․ Start on hands and knees in a neutral spine position․ Extend one arm and the opposite leg simultaneously, holding for a few seconds․ Slowly return to the starting position and repeat on the other side․ Perform 3 sets of 10-12 repetitions; This exercise enhances spinal stability, promotes proper posture, and reduces SI joint strain․ Progress by adding resistance or increasing hold time as strength improves․
5․3 Side Plank for Pelvic Stability
The side plank is an effective exercise for improving pelvic stability and SI joint health․ Lie on one side with legs stacked and feet flexed․ Lift hips off the ground, creating a straight line from head to heels․ Engage the core and hold for 10-15 seconds․ Perform 3 sets on each side․ This exercise strengthens the abdominal and pelvic muscles, enhancing spinal stability and reducing SI joint strain․ Progress by increasing hold time as strength improves․
5․4 Clamshell Exercise for Hip Muscles
The clamshell exercise strengthens hip muscles, improving SI joint stability․ Lie on your side with knees bent and feet touching․ Slowly lift the top knee while keeping feet together, squeezing hip muscles․ Hold for 3-5 seconds, then lower․ Perform 3 sets of 10-15 reps on each side․ This targets the gluteus medius, enhancing pelvic alignment and reducing SI joint strain․ Avoid arching your back; focus on controlled, pain-free movements to maximize benefits and support joint health effectively․

Phase 3: Advanced Dynamic Stabilization

Phase 3 focuses on advanced dynamic stabilization, incorporating functional movements to enhance SI joint stability and strength․ Exercises like single-leg stance and step-ups improve balance and coordination naturally․
6․1 Single-Leg Stance for Balance
The single-leg stance is an advanced exercise that enhances balance and stability․ Stand on one leg, keeping the other foot lifted slightly off the ground․ Hold for 30-60 seconds, focusing on proper posture and engagement of core muscles․ This exercise strengthens the SI joint and improves proprioception․ Perform 3 sets on each leg․ Ensure the pelvis remains level to avoid strain․ Progress by closing your eyes or using a soft surface for added challenge․
6․2 Step-Ups for Functional Strength
Step-ups target the hips and legs, enhancing functional strength and SI joint stability․ Use a sturdy step or platform, stepping up with one leg while keeping the other foot on the ground․ Ensure proper technique to maintain pelvic alignment․ Perform 3 sets of 10-12 reps per leg․ Gradually increase step height or add resistance as strength improves․ This exercise mimics daily movements, promoting better joint mechanics and reducing the risk of injury․ Focus on smooth, controlled motions for optimal results․
6․3 Dynamic Pelvic Tilts
Dynamic pelvic tilts enhance SI joint stability through controlled movement․ Start on your hands and knees in a neutral spine position; Slowly tilt your pelvis forward and backward, maintaining a smooth transition․ Repeat for 10-15 repetitions․ This exercise strengthens pelvic muscles and improves joint mobility․ Focus on maintaining control throughout the movement to avoid strain․ Regular practice helps reduce SI joint instability and enhances overall pelvic function․
6․4 Resistance Band Exercises
Resistance band exercises strengthen the muscles around the SI joint, improving stability․ Use a band to perform clamshell exercises, side steps, or banded pelvic tilts․ These exercises target hip and core muscles, enhancing joint support․ Start with light resistance and gradually increase intensity․ Focus on controlled movements to avoid strain․ Regular practice with resistance bands can improve SI joint function and reduce pain․ Always ensure exercises remain pain-free to promote healing and stability․

Creating a Home Exercise Program
Set realistic goals, track progress, and maintain consistency․ Schedule regular sessions with gentle exercises, ensuring safety and comfort․ Adjust as needed to optimize results and prevent discomfort․
7․1 Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is essential for a successful home exercise program․ Start by assessing your current abilities and health status․ Consult a healthcare professional to tailor objectives․ Break down larger goals into smaller, achievable steps․ Track progress weekly to stay motivated․ Celebrate milestones, no matter how small․ Adjust goals as needed to accommodate improvements or challenges․ Consistency is key, so ensure goals align with your lifestyle and commitment level․ This approach fosters sustainability and long-term success in managing SI joint health․
7․2 Frequency and Duration of Sessions
For effective SI joint exercise programs, aim for 2-3 sessions daily, with each session lasting 15-20 minutes․ Consistency is key to gradually improve joint stability․ Begin with shorter durations and increase as comfort allows․ Exercises should be performed at a comfortable pace, avoiding rushed movements․ Adjust frequency based on individual progress and comfort levels․ Regular practice helps maintain mobility and strength, supporting long-term SI joint health and reducing pain over time․
7․3 Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Regularly monitor your progress by tracking pain levels and mobility improvements․ Document the number of exercises completed and any changes in discomfort․ Adjust the intensity or duration of sessions based on your body’s response․ If pain increases, modify the exercises or consult a healthcare professional․ Celebrate small achievements to stay motivated․ Use a journal to record daily improvements, ensuring a tailored approach to your SI joint exercise program for optimal results and long-term relief․
7․4 Safety Precautions
Before starting SI joint exercises, consult a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying conditions or severe pain․ Begin with gentle movements to avoid aggravating the joint․ Stop exercises if pain exceeds 4/10 on the pain scale․ Avoid overexertion, as it may worsen symptoms․ Use proper technique to prevent strain․ Consider using supportive equipment like mats or belts for comfort․ Listen to your body and modify exercises as needed to ensure safety and effectiveness throughout your program․
Managing SI Joint Pain During Exercises
Manage SI joint pain with techniques like heat/ice therapy and gentle stretches․ Avoid movements causing sharp pain․ Consult a professional if discomfort persists or worsens during exercises․
8․1 Pain Management Techniques
Pain management techniques for SI joint exercises include using heat or ice therapy to reduce inflammation․ Gentle stretches and avoiding movements that exacerbate pain are crucial․ Monitoring pain levels ensures exercises remain safe and effective․ Techniques like deep breathing can help relax muscles, while activity modification prevents further strain․ If pain persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to adjust the exercise program and address underlying issues effectively․
8․2 Use of Heat or Ice Therapy
Heat or ice therapy can effectively manage SI joint pain․ Heat therapy, such as warm baths or heating pads, relaxes muscles and improves blood flow․ Ice therapy reduces inflammation and numbs the area, especially after acute injury․ Apply ice for 15-20 minutes, wrapped in a cloth to avoid skin damage․ Alternate between heat and ice based on symptoms․ Always consult a therapist to tailor therapy to individual needs, ensuring safe and effective pain relief during exercise routines․
8․3 Activity Modification
Activity modification is crucial to prevent SI joint pain aggravation․ Avoid heavy lifting, repetitive twisting, and prolonged sitting or standing․ Substitute high-impact activities with low-impact options like swimming or cycling․ Maintain proper posture to reduce strain on the joint․ Ergonomic adjustments at home and work can help alleviate discomfort․ Incorporate regular breaks during activities to stretch and move, ensuring joint mobility and pain management; Tailoring daily routines can significantly improve SI joint health and overall well-being․
8․4 When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help if SI joint pain persists despite home exercises or worsens over time․ Consult a healthcare provider if pain exceeds 4/10, radiates to the legs, or causes numbness/tingling․ Visit a physical therapist or chiropractor for guided treatment․ Severe cases may require medical interventions․ Don’t delay seeking help if activities of daily living become significantly impaired․ Early professional intervention can prevent further joint dysfunction and promote effective recovery․ Track symptoms to share with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan․
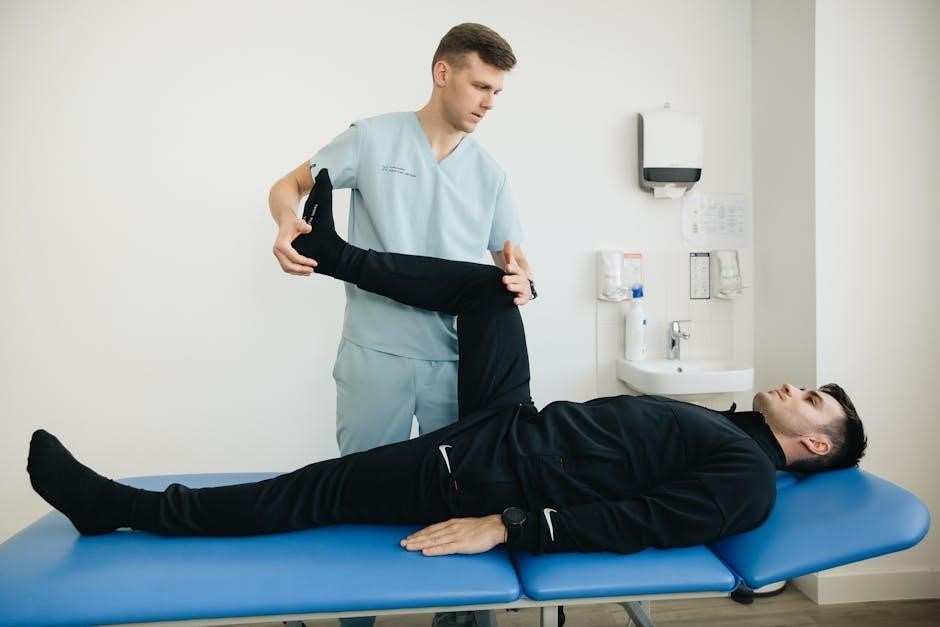
Additional Therapies and Treatments
Beyond exercises, therapies like physical therapy, chiropractic care, prolotherapy, and massage therapy enhance SI joint stability, address dysfunction, and support recovery, promoting overall well-being effectively always․
9․1 Physical Therapy for SI Joint Dysfunction
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in managing SI joint dysfunction, focusing on pain management, restoring function, and improving mobility․ Licensed therapists design personalized programs, incorporating exercises, manual therapy, and modalities․ Techniques include gentle mobilizations, stretching, and strengthening exercises to enhance joint stability and reduce discomfort․ The goal is to address biomechanical issues, promote healing, and empower patients with strategies for long-term management, ensuring a safe and effective recovery process tailored to individual needs and symptoms․
9․2 Chiropractic Care for Joint Mobilization
Chiropractic care specializes in joint mobilization, offering non-invasive techniques to restore SI joint function․ Chiropractors use spinal manipulations and adjustments to improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and alleviate pain․ These methods address misalignments and promote natural healing․ Often combined with exercises and ice/heat therapy, chiropractic care helps enhance joint stability and overall pelvic alignment, providing relief for SI joint dysfunction without medication or surgery, making it a popular choice for patients seeking holistic treatment options;
9․3 Prolotherapy for Joint Stability
Prolotherapy is a regenerative treatment that strengthens SI joint stability by stimulating natural healing․ It involves injecting a dextrose solution into the joint to promote ligament and tendon repair․ This non-surgical approach addresses chronic pain and instability, encouraging joint regeneration․ Often used alongside exercises, prolotherapy enhances joint function and reduces inflammation, offering long-term relief for SI joint dysfunction without the need for invasive procedures, making it a promising option for patients seeking alternative therapies․
9․4 Massage Therapy for Muscle Relaxation
Massage therapy is a complementary treatment that targets muscle tension around the SI joint․ Techniques like deep tissue massage and myofascial release help relax tight muscles, improve circulation, and reduce stiffness․ Regular massage can alleviate pain and discomfort, making it easier to perform SI joint exercises․ It also helps break up adhesions in soft tissues, promoting joint mobility and stability․ Massage therapy is often recommended alongside physical therapy for comprehensive pain management and enhanced recovery․
SI joint exercises offer a natural path to healing and stability․ Consistent practice enhances mobility and pain relief․ Explore additional resources for continued learning and support․
10․1 Summary of Key Points
SI joint exercises are essential for improving sacroiliac stability and reducing pain․ A structured approach, including gentle stretches, strengthening, and advanced stabilization, promotes healing and mobility․ Consistency, pain-free practice, and proper progression are crucial․ Techniques like pelvic tilts, glute bridges, and core engagement enhance joint function․ Natural therapies, such as physical therapy and massage, complement exercise programs․ Tracking progress and seeking professional help when needed ensures long-term relief and optimal joint health․
10․2 Encouragement for Consistent Practice
Consistency is key to achieving lasting relief from SI joint pain․ Regular practice of exercises, even for short periods, can significantly improve stability and reduce discomfort․ Celebrate small progress and remind yourself of the long-term benefits․ Stay motivated by focusing on how these exercises enhance your daily activities and overall well-being․ With patience and dedication, you can maintain a pain-free, active lifestyle․ Keep moving forward confidently, knowing each effort brings you closer to optimal joint health and mobility․
10․3 Resources for Further Learning
Downloadable PDF guides, such as those detailing sacroiliac joint exercises, provide comprehensive routines and tips for managing pain․ Research studies and articles offer deeper insights into SI joint dysfunction and treatment options․ Websites specializing in physical therapy and orthopedics often feature instructional videos and downloadable resources․ Explore these tools to enhance your understanding and practice of SI joint exercises for long-term relief and improved joint stability․
